1j24b various triode connections.
1j24b various triode connections.
Fellow radiophiles:
One of the characteristics of Russian Subminiature Tubes is a very efficient screen grid G2 design that takes only a small proportion (~10%) of the total plate current. This low G2 current makes it attractive to try various triode-connected circuits to achieve different values of triode intrinsic gain μ by choosing different feedback networks between the plate and G2.
This concept of turning a pentode into a triode with a particular intrinsic gain μ is similar to the method of making a FET behave like a triode with a trioderizer circuit.
 The basic concept is to provide external negative feedback (NFB) from the plate to the the screen grid G2, which is similar to the internal negative feedback from the plate of triode to the field surrounding the space charge at the cathode.
The basic concept is to provide external negative feedback (NFB) from the plate to the the screen grid G2, which is similar to the internal negative feedback from the plate of triode to the field surrounding the space charge at the cathode.
Having G2 as a low input current control element, leaves the control grid free to be used with very high impedance source circuits.
The 45V source can be used independently from the negative feedback network to control the equivalent transconductance gm of the triode.
The following curve trace families were taken with the Tektronix TEK575 transistor curve tracer and show several triodes that can be emulated with this pentode.
Anode shorted to G2 gives the native μ=20. R1=3.3Meg R2=1Meg gives μ=80
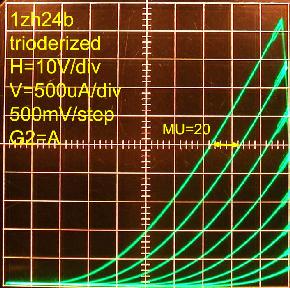
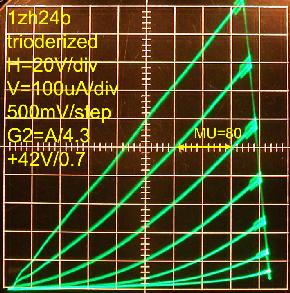
Reducing NFB with R1=5Meg gives μ=104 Lastly, R2=10Meg gave μ=180

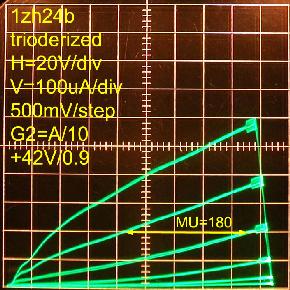
Note that the top trace in all of these plots is for G1=0V. The lower traces have negative G1 voltages in -500mV steps. But the control grid G1 remains non-conductive below -1V. See 1zh24b DC operation at low voltage for more details about G1 conduction.
Best regards,
-Joe
To thank the Author because you find the post helpful or well done.
