- Country
- Switzerland
- Manufacturer / Brand
- Albis, Albiswerke AG (Siemens Switzerland AG / Telefunken Zürich AG / Siemens-Albis); Albisrieden
- Year
- 1984–1993
- Category
- Signal Processing and Computing
- Radiomuseum.org ID
- 305347
Click on the schematic thumbnail to request the schematic as a free document.
- Wave bands
- - without
- Power type and voltage
- Powered by external power supply or a main unit. / 6 Volt
- Loudspeaker
- - - No sound reproduction output.
- Material
- Metal case
- from Radiomuseum.org
- Model: Mac-CC 392 - Albis, Albiswerke AG Siemens
- Shape
- Rack
- Dimensions (WHD)
- 34 x 222 x 309 mm / 1.3 x 8.7 x 12.2 inch
- Notes
-
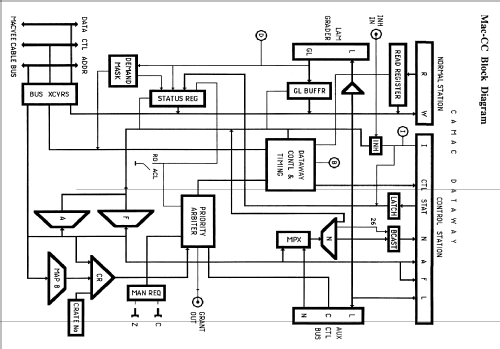
Defined jointly in 1972 by the U.S. NIM and European ESONE Committees, CAMAC (Computer Automated Measurement and Control) is a modular data handling system used at research laboratories and industrial sites all over the world. Mac-CC is a CAMAC crate controller for Macintosh computers. With the appropriate interface cards, such as A410 MICRON for the Macintosh II family, it can be connected to all models of the original closed Macs, and all the later open modular Macs that used the Apple NuBus.
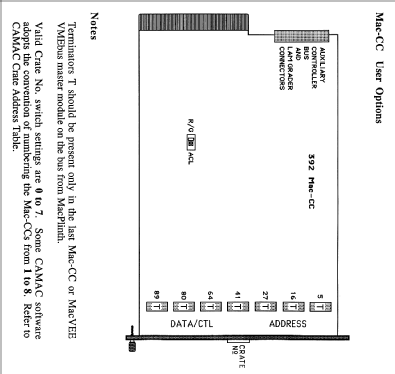
The double-width module contains two printed circuit cards with 86-contact edge connectors, a main card that plugs into the rightmost control station and a daughter card that plugs into the adjacent normal station in a CAMAC crate. Up to 8 Mac-CCs can be daisy-chained on a pair of Data/Control and Address twisted-pair ribbon cables from the Macintosh interface, and the cables can be over 50m long. The crate numbers are selected by a thumbwheel switch on the front panel, and plug-in terminators should be present only in the last Mac-CC of the chain. There are front panel push-buttons for manual Initialize (Z) and Clear (C) operations, as well as an Inhibit signal input (Lemo I) and status LEDs for Dataway Busy (B), Demand (D) and Inhibit (I).
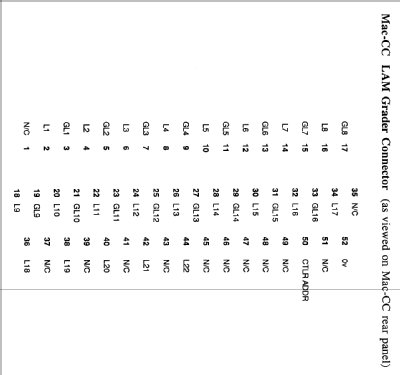
Connectors on the rear panel provide for links to an optional LAM grader and auxiliary controller in the CAMAC crate, and the selected priority arbitration mode (R/G or ACL) can be read at any time in the Mac-CC status register. As Mac-CC has a higher priority than any auxiliary controllers in the crate, only a Grant-out signal is provided at the front panel (Lemo G). The ACB Request signal is functionally connected to the Grant-in of the Mac-CC arbiter internally. In response to an ACL generated by an auxiliary controller, Mac-CC always completes the current CAMAC cycle before relinquishing control.
Mac-CC receives LAMs L1 - L23, and transmits the 23-bit LAM pattern to the ACB. It also transmits L1 - L22 to an optional LAM Grader and receives the demand pattern GL1 - GL16 after patching and masking in that unit. Alternatively, simple demand patching may be effected directly at the Mac-CC LAM Grader connector. Demand Present is generated if any GL bit is asserted. If in addition the Mac-CC Demand Output is enabled, a Level-7 Macintosh interrupt is generated, which is auto-vectored through $7C - $7F. During interrupt service, Macintosh reads the demand pattern by N(30).A(0-7).F(0).
Mac-CC was designed by Bruce Taylor and manufactured by Siemens-Albis SA. The controllers were used from 1984 until the mid-1990s, when new Macintosh models changed from Apple NuBus to PCI bus.
- Net weight (2.2 lb = 1 kg)
- 1.2 kg / 2 lb 10.3 oz (2.643 lb)
- Author
- Model page created by Bruce Taylor. See "Data change" for further contributors.
- Other Models
-
Here you find 176 models, 151 with images and 145 with schematics for wireless sets etc. In French: TSF for Télégraphie sans fil.
All listed radios etc. from Albis, Albiswerke AG (Siemens Switzerland AG / Telefunken Zürich AG / Siemens-Albis); Albisrieden