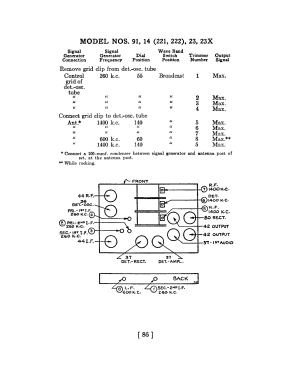
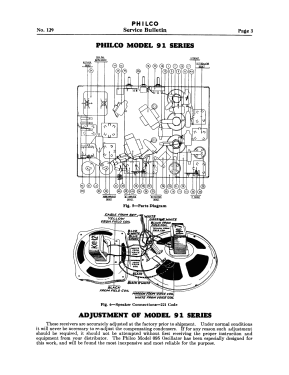
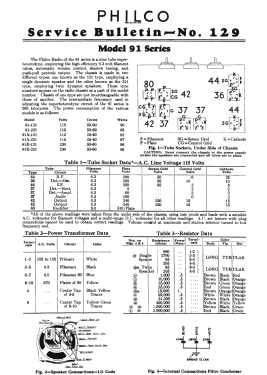
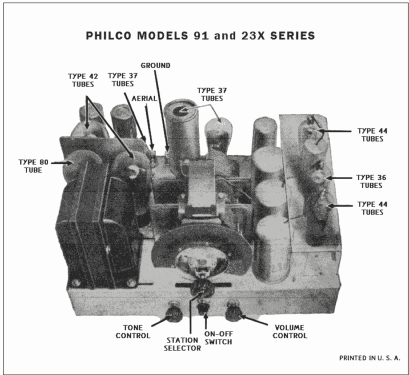
91D (91, 91A, 91E) Late
Philco, Philadelphia Stg. Batt. Co.; USA
- Country
- United States of America (USA)
- Manufacturer / Brand
- Philco, Philadelphia Stg. Batt. Co.; USA
- Year
- 1933
- Category
- Broadcast Receiver - or past WW2 Tuner
- Radiomuseum.org ID
- 140822
Click on the schematic thumbnail to request the schematic as a free document.
- Number of Tubes
- 9
- Main principle
- Superhet with RF-stage; ZF/IF 260 kHz
- Wave bands
- Broadcast (MW), Police, sometimes also early TV (75-200m).
- Power type and voltage
- Alternating Current supply (AC) / 115 Volt
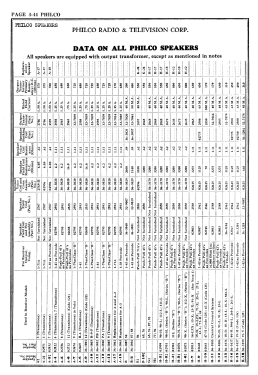
- Loudspeaker
- Electro Magnetic Dynamic LS (moving-coil with field excitation coil)
- Material
- Wooden case
- from Radiomuseum.org
- Model: 91D [Late] - Philco, Philadelphia Stg. Batt
- Shape
- Console, Highboy (legs > 50 %).
- Notes
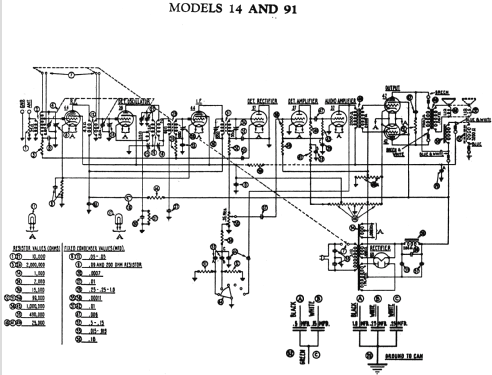
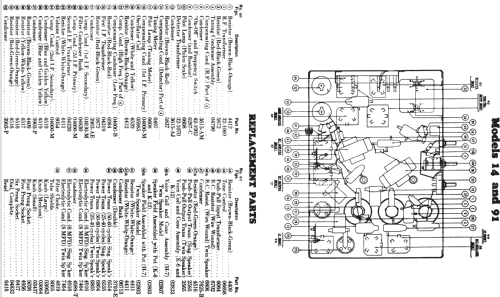
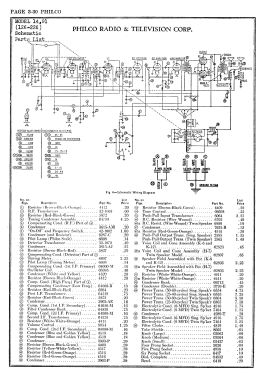
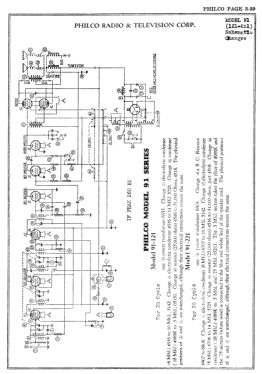
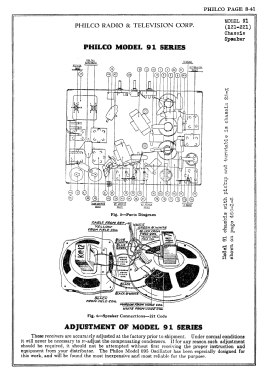
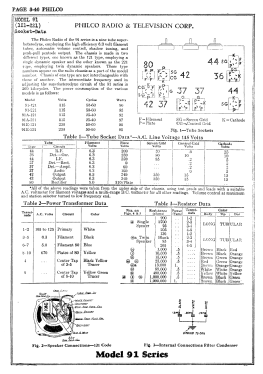
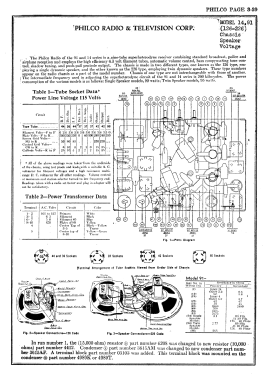
- The model 91 series uses a 9-tube chassis in a variety of different cabinet styles. There are three chassis types depending on power requirements: 91 (115 VAC 50-60 Hz), 91A (115 VAC 25-40 Hz), and 91E (230 VAC 50-60 Hz). Early versions of the chassis are single band (BC only) and late versions are dual band (BC and 1.5 - 3.2 MHz police band). All versions include a shadow meter (tuning aid) and were among the first to use this feature. On 2-band models, the bandswitch is integrated with the power switch (adding a third position to the switch).
Chassis codes are as follows:
Codes 121 and 123 - single band, single speaker
Code 221 - single band, dual speaker
Code 126 - dual band, single speaker
Code 226 - dual band, dual speaker
There were a number of changes in cabinet styles, which, along with changes in the chassis, result in a complex series of models in this family.
Model 91B is a cathedral using one of Philco's classic cathedral designs with spade-shaped speaker opening and recessed panel. The early version of 91B has the single band chassis, and the late version has the dual-band chassis.
Model 91L is a lowboy. The early version has an arched control panel, short legs, and a pair of vertical bars on each side of the speaker opening. The early version uses the single band chassis. The middle version has the same cabinet, but with the dual band chassis. The late version has the dual band chassis in a new cabinet style with four longer legs interconnected by a cross brace.
Model 91H is a highboy. The early version has a roughly square speaker opening with two embellished vertical bars, and the cabinet has six legs interconnected by a full box bracing system at the bottom of the legs. The middle version has the same cabinet, but with dual band chassis. The late version has the dual band chassis in a new cabinet with a shield-shaped speaker opening, and a less complex bracing system at the bottom of the legs (no brace between the two front legs).
Model 91D is a highboy with doors, which also has three versions analagous to 91H (similar use of single vs. dual band chassis and simple vs. complex leg bracing).
Model 91X is a floor-type console with inclined sounding board and dual speakers (other models are single speaker). The early version uses the single band chassis and has a large open sounding board. The middle version uses the same cabinet but has the dual band chassis. The late version has the dual band chassis in a new cabinet style with pillars in front of the sounding board.
Model 91RX is a chairside with a separate speaker cabinet. The control unit resembles a table on four legs with controls on top, and the speaker cabinet has a large inclined sounding board with pillars. Ramirez mentions that some models of 91RX may have had dual speaker, although most had a single speaker.
- Price in first year of sale
- 85.00 $
- Source of data
- Philco Radio 1928-1942
- Circuit diagram reference
- Rider's Perpetual, Volume 3 = 1933 and before
- Literature/Schematics (1)
- Philco 1928-36 Wiring Diagrams, Parts Lists, and Essential Service Data
- Author
- Model page created by Thomas Albrecht. See "Data change" for further contributors.
- Other Models
-
Here you find 4063 models, 2220 with images and 3710 with schematics for wireless sets etc. In French: TSF for Télégraphie sans fil.
All listed radios etc. from Philco, Philadelphia Stg. Batt. Co.; USA